Remelting Steel for the Highest Demands: Electro Slag Remelting and Vacuum Arc Remelting
Daniel Kipp
When it comes to applications with high quality demands, remelting steel can provide the answer. In this article, you'll learn why this is and we'll introduce the two main processes for remelting steel – electro slag remelting (ESR) and vacuum arc remelting (VAR).
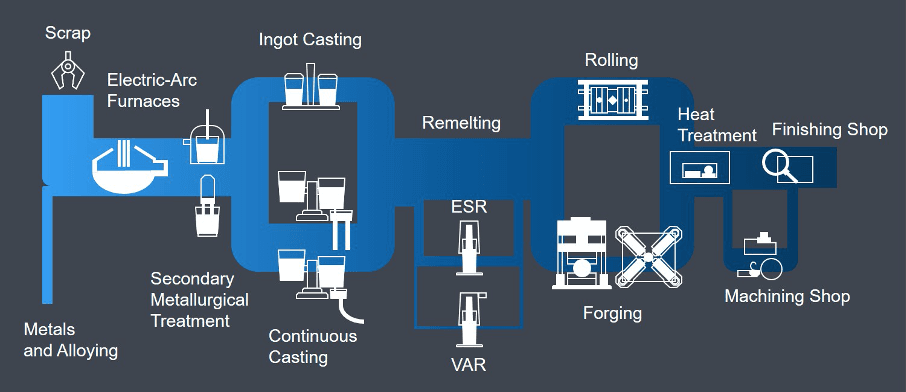
Figure 1: Perfect manufacturing workflow and added value at DEW
The main purpose of the remelting process is to clean the steel. In short: in the ESR process all oxidic particles are absorbed by the slag when the metal drops pass through the remelting slag. Apart from the deposition of macroscopic inclusions, the microscopic cleanliness is also significantly improved. By remelting under inert gas the oxide cleanliness can be additionally improved. For further optimization of microscopic cleanliness, the VAR process is used. For the most demanding applications, ESR and VAR processes can be combined.
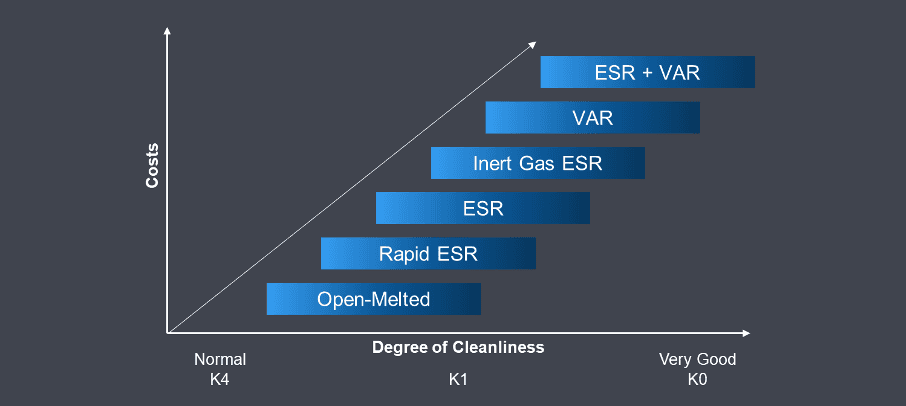
Figure 2: Costs and degree of cleanliness depending on remelting process (schematic)
The ESR process
Melting of a consumable electrode, which is immersed in liquid slag, occurs in ESR furnaces. The current running through the slag via the electrode heats up the slag due to its high electrical resistance to the point that the tip of the electrode, which is immersed in the slag, is liquefied. The steel dripping from the electrode is then freed from contamination when passing through the liquid slag. Oxides and sulphur are bound in the slag. After passing through the slag the steel solidifies again to form a remelted block. The remelting process takes place in a water-cooled copper mold, so that the block solidifies quickly and very uniformly. The slag that gave this process its name mostly consists of a mixture of fluorspar, chalk, and clay.
The VAR process
The VAR process has continuously gained importance in the past decades and has gained a firm position for producing high-quality speciality steel. During the remelting process a consumable electrode is melted under a vacuum. The energy required for melting is created by applying an electric current, which generates an arc between the electrode tip and the metal sump below, produced by the molten ingot. Remelting occurs under vacuum at a pressure of only approx. 0.001 mbar. The lower part of the remelting unit consists of a water-cooled copper mold, which ensures uniform heat dissipation and even solidification. In this mold the resultant remolten ingot grows to the extent the electrode melts. In addition, through this process, undesired accompanying elements are evaporated and oxidic inclusions are removed.
Looking into the inside
Low remelting speed combined with the water-cooled mold ensures a particularly homogeneous and balanced/stable solidification. The segregations within a remelted ingot are thus much lower than in open cast continuous cast billets or conventional ingots. For this reason, most segregation-sensitive steels are remelted for homogenization.
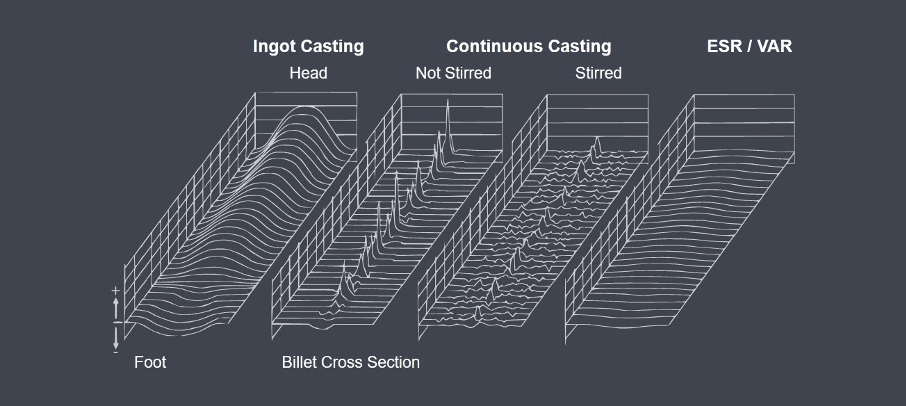
Figure 3: Segregation profiles in billets of ingot casting, continuous casting and ESR/VAR (schematic)
If you are interested in special steel solutions from Deutsche Edelstahlwerke, get in touch with them on Matmatch today.
Artikel von <a href=/suppliers/dest-deutsche-edelstahlwerke-dew-> Deutsche Edelstahlwerke (DEW) </a>Deutsche Edelstahlwerke (DEW)
Deutsche Edelstahlwerke (DEW) is one of the world’s leading producers and processors of special steel long products and belongs to the Swiss Steel Group. In the three materials groups – engineering steel, tool steel and stainless, acid and heat resistant steel – Deutsche Edelstahlwerke offers international customers a uniquely wide range of product dimensions, from drawn wire with a diameter of 4.5 mm to open-die forgings with a diameter of 1,100 mm. As a partner with technical competence in steel, Deutsche Edelstahlwerke develops innovative, individual special steel solutions for complex high-tech applications and offers services ranging from steelmaking to extensive steel processing and steel finishing.
Four of the best
Deutsche Edelstahlwerke is the leading producer of long high-grade steel products. The products range from drawn wire with a diameter of 5.0 mm all the way to forged products with a diameter of 1100 mm.
This wide product range makes our offering unique in the world and gives our customers a decisive advantage: with us, they can get everything from a single source.
Tool steels
As one of the world's largest producers of tool steel, we supply exactly the steels that our customers need for their individual products, with properties accurately tailored to the respective application.

Stainless, acid and heat-resistant steels
Stainless, acid and heat-resistant steels from Deutsche Edelstahlwerke are always in demand when extreme technical requirements are imposed on the material. Because of their outstanding chemical corrosion and mechanical properties, these steel grades are particularly used in the chemical industry, mechanical engineering, the food processing industry, power engineering, medical equipment, traffic engineering and the offshore sector.

High-grade structural and anti-friction bearing steels
Automotive engineering, mechanical engineering and gearbox construction would today be almost inconceivable without high-grade structural steels and anti-friction bearing steels from Deutsche Edelstahlwerke. Made-to-measure processing and service properties are achieved by precise setting of the chemical composition and by special production and test conditions.

Special materials
Ferro-Titanit is the name of the carbide-alloyed materials of Deutsche Edelstahlwerke produced by powder metallurgy, uniting the properties of steel and cemented carbides.


