What is Burnishing and What is it Used for?
Burnishing is the process of rubbing metal with a small hard tool, which can be either a ball type or roller type, to compact the surface. It is a very useful finishing technique that can increase the workpiece surface finish as well as add microhardness. Burnishing is also known by various other names such as:
- Superfinishing process
- Ballizing process
What is burnishing?
The burnishing process is one of the more advanced finishing techniques in which no chips are produced and material is not removed from the surface of the workpiece.
It is dependent on pressing a rolling tool against the workpiece surface. Plastic deformation or physically changes of a surface, due to sliding contact with another object, is achieved using this technique.
The process of burnishing can be done using a sliding surface when the local contact stress exceeds the yield strength of the material.
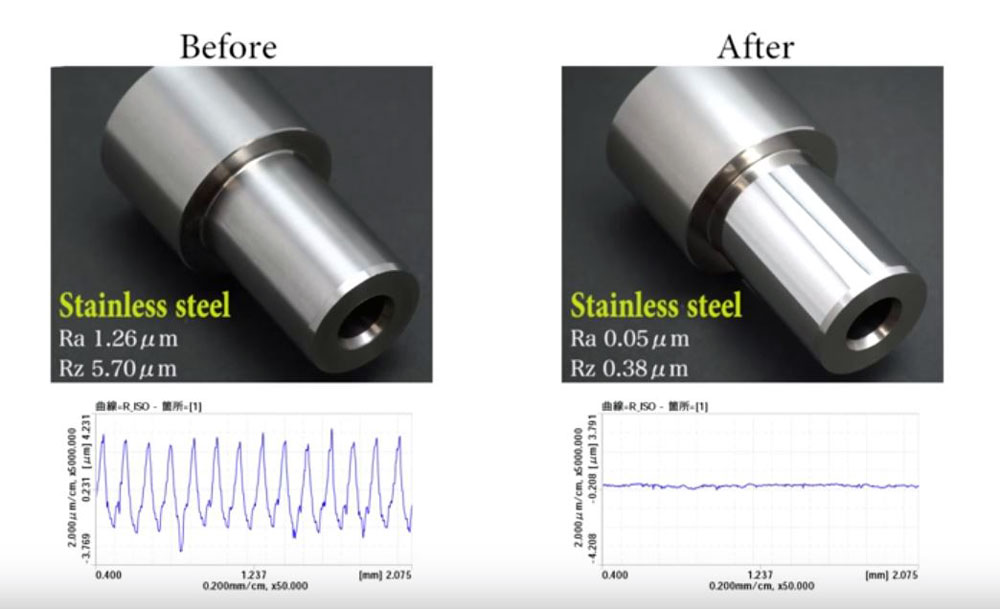
Burnishing can be carried out in a number of different ways. It simply requires rubbing the burnishing tool with the workpiece with enough force to produce the plastic deformation. You can use a dedicated machine for this purpose or it can be done on a regular lathe or milling machine.
In dedicated machines, the tool is attached to a motor that rotates around the workpiece. The workpiece is attached to the machine using a wise or magnetic table. When the rotating burnishing tool touches the workpiece it applies a degree of force. As the workpiece is moving from left to right, the process of burnishing will take place.
There are two main ways to inspect and rate the burnishing process:
- Surface inspection by the naked eye
- Direct measurement using an appropriate instrument
The direct measuring option is able to determine a numerical value to the surface finish allowing you to compare and contrast with other burnishing processes.
The most popular instruments used are stylus probes which operate on electrical principles. Moving the stylus generates a voltage signal, and there are pneumatic elements used to measure the actual surface finish.
Process variations
There are two main ways in which burnishing is executed which are known as:
- Roller burnishing
- Ball burnishing
Roller burnishing
This is a cold working process technique, which produces a super finish/fine surface when hardened rollers are moved/turned on the surface of the material.
Ball burnishing
Ball burnishing creates a super finish often used when looking to produce a specific colour/luster on the surface of the workpiece. In this process, a hard ball is pressed against the workpiece surface.
Materials that can benefit from burnishing
The burnishing process is mostly carried out on soft metals such as aluminum, brass, zinc and plastics. It can also be performed on low carbon steel alloys.
Applications for burnishing
The process of burnishing is regularly used with an array of different products such as:
- Cutting tools
- Turbine blades
- Airfoils
- Curved pipes
- The field of medicine
- Capillary tubes
- Sanitary pipes
- Optics
- Food industry
- Needles
Mechanical design guidelines
- The value of the surface roughness value (ra) is measured between 0.04 and 0.8 μm
- The burnishing process creates a surface roughness measurement from 0.8 mm to 2.5 mm.
- As it is a non-machined process, the deformation will vary with the changes of pressure/force when contact is made with the surface.
- The shape/texture obtained using burnishing is irregular.
- Surface irregularity of the non-working surface also matters in the process of burnishing.
- The direction of the lays will depend upon the method used.
Economics of the burnishing process
- Very low equipment costs – in some cases, no special machines or tools are required
- Production rate is very low – not recommended where high volumes are required
- Automation of the process is possible – this can increase output but may increase production costs
- Low energy consumption
- No wastages of material – potential for cost savings
- Lubrication is not required in this process – reducing overall costs
- This cold working process is more cost-effective compared to a hot working process
- There is potential for significant time savings when compared to other processes
Advantages of burnishing
- Less time is required for this process
- No material is removed, so no waste is produced
- Easy to control all steps of this process
- Low noise
- Suitable for use on all machine tools
- No additional lubrication required
- Creates longer-lasting tools
- No wear of bearings, no need for slideway
- No significant dimensional changes
- Coolant is not required during the process
- No dust/mud is created
Disadvantages of burnishing
- This process is not suitable for all ordinary finishing tasks – other conventional techniques may be more appropriate
- There may be cost implications to consider against more traditional, perhaps less successful, methods
- The wise/magnetic tables are not appropriate for mass production
- A numerical assessment is required to check the smoothness of the finish
Sources
[1] Engineering metrology by Er. R.K Jain Khanna publisher.
[2] Environmental engineering (McGraw hill series) by Howard S Peave