Bosch develops challenging ceramic micro-reactor in additive manufacturing
Bosch Advanced Ceramics
- Bosch Advanced Ceramics produces sophisticated ceramic micro-reactor for high-temperature applications using the 3D printing process.
- The reactor was developed in a joint project with BASF and KIT.
- 3D-printed technical ceramics withstand high demands of chemical reactions.
Together with the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and the chemical company BASF, Bosch Advanced Ceramics has developed a complex micro-reactor made of technical ceramics for high-temperature reactions and produced it using additive manufacturing. Microreactors, which are often used to research the fundamentals of chemical-technical processes, have to withstand the harshest conditions.
Only by combining the additive manufacturing method (3D printing) and the special material properties of the technical ceramics could the demanding technical requirements of the customer BASF ultimately be mapped. The use of additive manufacturing enables the design and construction of very small flow channels (0.5 mm channel width) for the chemical reactions inside the reactor.
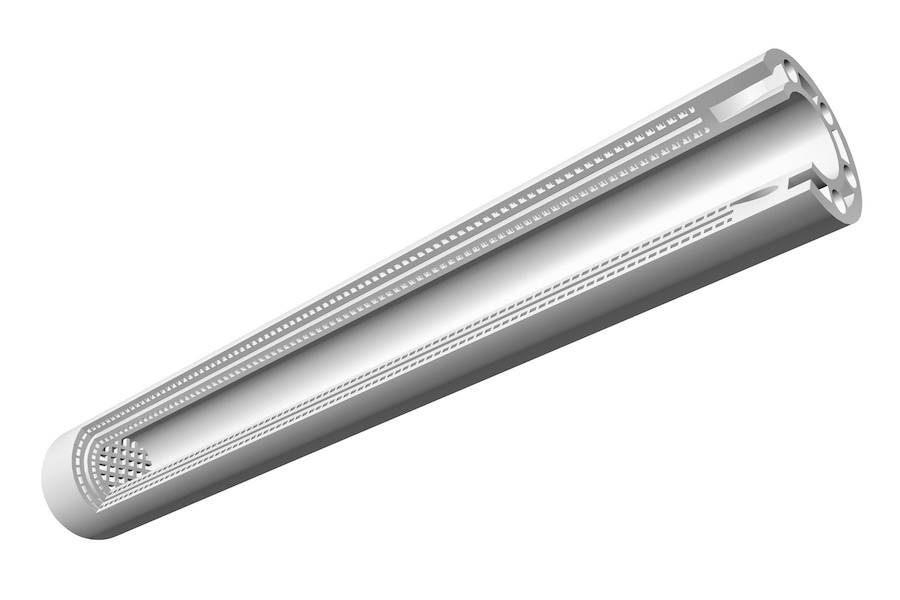

Figure 1. Microreactor BASF/KIT with internal channels/cross-section
|
Dimensions |
|
|
Component height |
107 mm |
|
Component diameter |
16 mm |
|
Channel width |
0.5 mm |
|
Bar dimensions |
0.3 mm |
Technical ceramics deals with specific reaction conditions
Due to its unique properties, such as strength, temperature-, abrasion- and corrosion resistance, BASF and KIT chose aluminum oxide as material.
This material is ideally suited to meet all the requirements placed on the component. The heat resistance and high strength of the material allow it to work safely under extreme process conditions. The thermal conductivity of 37 W/mK allows good temperature control, and the material's low thermal expansion of 7x10-6 K-1 helps to ensure that only minor distortions occur in the apparatus, even with large temperature differences. In actual reactor design, this is particularly important with regard to the outer cooling jacket. In this area of the design, a temperature drop of several 100 K per millimeter occurs during operation.
Depending on the reactant inside the reactor, the corrosion resistance of the reactor is advantageous. A long service life can be achieved through the use of ceramics. This is also an important economic aspect.
Moreover, the low electrical conductivity and translucency of the ceramics make the interior of the reactor accessible to various measurement and control techniques that cannot generally be used with reactors made of metal.
|
Advantages of ceramic 3D printing:
|
Additive manufacturing enables the production of complex and precise components
In principle, manufacturing by means of 3D printing involves higher costs than conventional techniques, such as injection molding, turning, milling or similar. Without additive manufacturing, a ceramic reactor with such elaborate internal structures could not be produced at a reasonable cost.
Only 3D printing thus makes it possible to redesign components since structures specially adapted to the process or to the necessary function can be realized with greater flexibility - true to the principle of process-specific apparatus engineering. For the KIT and BASF microreactor, this means in specific terms that the temperatures and material flows in the reactor can be controlled particularly precisely with this structure, thus opening up new possibilities for optimizing reactions.
The competence of Bosch Advanced Ceramics in terms of mastering the manufacturing process and the know-how about necessary design adaptations, which ensure functionality and producibility, essentially contributed to a successful implementation.
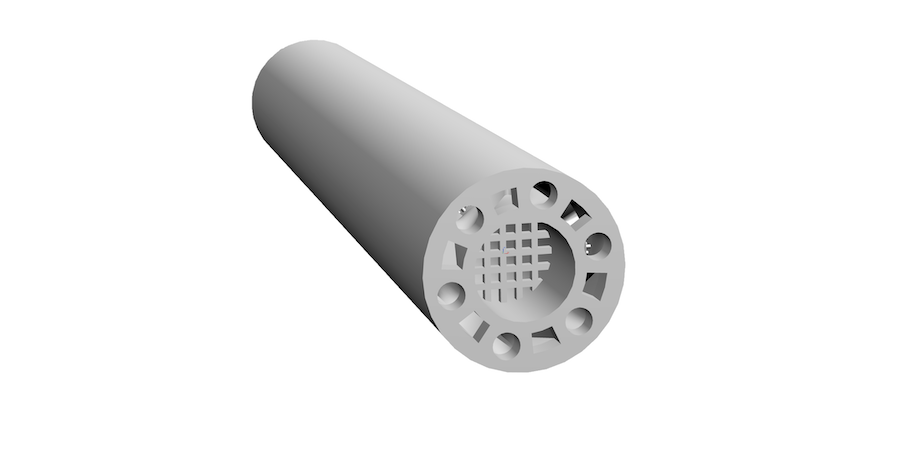

Figure 2. Micro-reactor: Whole component
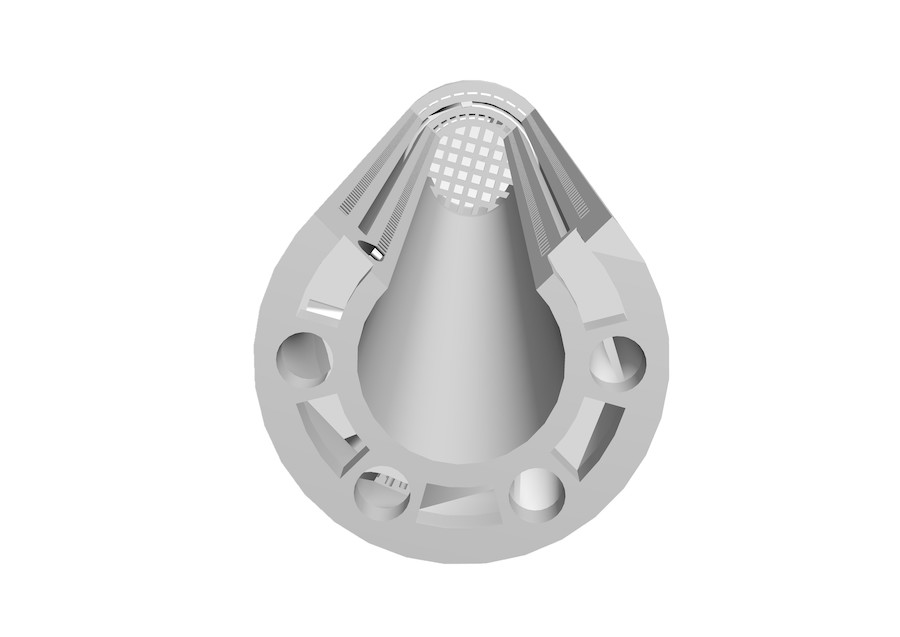
Figure 3. Micro-reactor: Cross-section
About Bosch
Bosch is world-renowned for its quality and precision in advanced ceramics for the automotive sector. Bosch Advanced Ceramics now enables the use of these advanced ceramics in new markets and offers functional ceramics for the food goods, industrial goods, electrical and medical sectors. The combination of innovative production capabilities and Bosch's proprietary materials makes it possible to produce unique and precise ceramic products for a wide variety of markets. The demand for ceramic products is continuously increasing: the requirement is higher complexity combined with precision and economy. At this interface, Bosch Advanced Ceramics sets the new benchmark with innovative production technologies.
Artículo de <a href=/suppliers/bosc-grow-platform-gmbh-a-bosch-company-advanced-ceramics> Grow Platform GmbH (a BOSCH company) Advanced Ceramics </a>Grow Platform GmbH (a BOSCH company) Advanced Ceramics
Bosch is world-renowned for its quality and precision in the field of advanced ceramics for the automotive sector. Bosch Advanced Ceramics, the ceramics division of grow platform GmbH, now enables the use of these advanced ceramics in new markets and offers functional ceramics for the household, industrial, electrical, engineering and medical sectors. The combination of innovative production capabilities and Bosch's proprietary materials makes it possible to develop unique and precise ceramic products for a wide variety of markets. The demand for ceramic products is continuously increasing: the requirement is higher complexity combined with precision and economy. At this interface, Bosch Advanced Ceramics sets the new benchmark with innovative production technologies. Ceramic injection molding in combination with inmoldlabeling for functional layers and 3D printing enables the production of complex structures while taking into accountthe highest precision and almost unlimited possibilities in design for use in a wide range of applications - from batch size 1 to large series. Depending on the application, three different materials are available. Zirconium oxide, high-purity aluminum oxide and ZTA are the basic materials for ceramic injection molding or 3D printing. Of course, we are also happy to use other technologies and materials accessible to us to meet your challenge. Here we can draw on existing expertise from the spark plug and lambda sensor sectors.

Spiral-Mixer:
Seamless spiral mixer manufacturing in one piece.
This mixer cannot be manufactured by ceramic injection molding or pressing.
Only additive manufacturing is able tocreate such geometries.
This component is mainly used in the chemicalindustry.
It is used to control the flow of corrosive liquids and gases.
The turbine rotor has the following dimensions:
- Height: 25 mm
- Diameter: 10 mm
- Wall thickness: 0,3 mm
Advantages and application areas of the turbine rotor:
- very good shaft - hub connection
- Extremely good stress distribution
- uniform expansionas well as compression
- High temperature ranges
- speeds in very high range possible
- There is no need to balance it, because it is made in one piece

Sugar-Cube/ Ring with channels:
Ceramic 3D printing enables finest internal channels and structures!
In process technology for example an optimized flow behavior is crucial for a high yield.
Through this production process we can produce complex structures to guide the fluid wherever it needs to go. No matter how intricate the path.
in additionadvanced ceramics provide an ideal thermal management even at high temperatures and combined with cooling fluids entire assembly groups can be realized in a single 3D printed component.
Dimensions:
Ring with channels:
Outer diameter: 12.45 mm
Height: 8,2 mm
Internal channels: 0,7 mm

Sugar cube:
Openings: 0.4 mm
Edge length: 11,5 mm x 8,3 mm

Heat-Exchanger:
If you want to work with high corrosive combustion air or liquidsyou can use this kind of ceramic heat exchangers.
Maybe you have also looked intoCeramic materials. But due to the design limitations of conventionally produced Ceramics many heat exchanger designs were not possible.
3dprintingof Ceramics has proven to be a gamechangerin the design of ceramic components.
Especially for Heat exchangers with very thin channels we can provide a solution that is tailored exactly to your use case!
With our additive manufacturing technologywe are able tocreate internal channels as thin as 1 mm to ensure that you can reach exactly the spot, where you need to remove the heat.
Since we don’t have to machine those channelsit doesn't matter if those channels are straight, bend or a maze.
Dimensions::
Outer diameter -> 20 mm
Component height -> 25 mm
channel diameter -> 1.4 mm

Functional coatings
Durable coatings to extend functionality
Coatings on technical ceramics can have different objectives: Either the existing properties are improved, for example by applying friction-reducing layers, or entirely new properties are added. For example, ceramics – actually an insulating material – can be made conductive at certain points by applying metallic layers. These layers are permanently bonded to the ceramic base material by sintering. The ceramic can thus be used for completely new applications.
Wide range of coating materials and technologies
Depending on the materials used, the coating can be sintered together with the component at high temperatures (co-firing); or the coating is applied to the already sintered component. Then sintering must be carried out again at lower temperatures (post-firing). Co-firing achieves better layer adhesion, but cannot be used with all materials. Bosch Ceramics has already realised many coatings, for example with gold, silver, platinum, chrome but also hard materials such as DLC. The wide range of coating technologies ensures an extensive choice of materials here.
Our processes for functional coatings
In-mold labelling
With In-mold labeling, a film with printed coatings is placed in an injection molding tool and then encapsulated with ceramic material. The film is removed in the subsequent processes, while the functional coating is permanently bonded to the ceramic.
Tampography
With this process, coatings can be applied using a flexible silicone die to non-planar ceramic components, such as curved surfaces.
Screen printing
With screen printing, metallic pastes can be applied with great precision to flat components. For electronics, this means producing multi-layer circuits with ceramic carrier plates (LTCC technology).
CVD
With chemical vapor deposition, highly complex parts can be refined with precise layers on a three-dimensional level. Advanced Ceramics works sustainably using unique processing techniques to avoid the formation of harmful hexavalent chromium.
PVD
The technically demanding process of physical vapor deposition achieves excellent layer adhesion, producing thin, compact coatings in a wide variety of materials.



