AISI 304 (1.4301) Stainless Steel
What is AISI 304?
AISI 304 (1.4301) is a widely-used austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel. It has excellent drawing properties and very good formability, while it is also highly corrosion-resistant. Typical uses of 304 stainless steel include sinks, kitchen equipment such as pans, tubing and much more.
Type 304 is sometimes also referred to as 18/8, a moniker that comes from its typical composition of 18% chromium and 8% nickel. Other elements in the alloy include nickel, manganese, silicon, nitrogen, carbon, phosphorus, and sulphur.


Chemical Composition of AISI 304
AISI 304 typically contains 17.5-19.5% chromium, 8-10.5% nickel, 2% manganese, 1% silicon, 0.11% nitrogen, 0.07% carbon, 0.05% phosphorus, and 0.03% sulphur.
Table 1. Chemical composition of AISI 304 stainless steel
Element |
Weight |
|
Iron |
66.74 - 71.24% (Balance) |
|
Chromium |
17.5 - 19.5% |
|
Nickel |
8 - 10.5% |
|
Manganese |
2% |
|
Silicon |
1% |
|
Nitrogen |
0.11% |
|
Carbon |
0.07% |
|
Phosphorus |
0.05% |
|
Sulphur |
0.03% |
Equivalents and other designations of AISI 304
The following are all equivalents of AISI 304:
X5CrNi18-10, EN 1.4301, DIN 1.4301, UNS S30400, BS 304S15, BS 304S16, BS 304S31, BS EN58E
Properties of AISI 304
The table below shows some of the most common material properties of AISI 304.
|
304 (Typical values at 20°C) |
304 Annealed (Typical values at 20°C) |
|
|
Density |
8 g/cm³ |
|
|
Elastic modulus |
193 GPa |
200 GPa |
|
Hardness, Brinell |
215 HB |
|
|
Tensile strength |
500-700 MPa |
590 MPa |
|
Yield strength |
190 MPa |
240 MPa |
|
Elongation |
40% |
|
|
Coefficient of thermal expansion |
1.72E-5 1/K |
|
|
Thermal conductivity |
16.2 W/(m·K) |
|
|
Melting point |
1450°C |
|
|
Specific heat capacity |
500 J/(kg·K) |
|
|
Electrical resistivity |
0.73 x 106 Ω·m |
In addition to the material properties mentioned above, AISI 304 has good technological properties, such as corrosion resistance and machinability.
Corrosion resistance
AISI 304 is highly corrosion resistant to most oxidizing acids. However, corrosion can occur in environments containing chlorides. 304 stainless steel is not as corrosion-resistant as 316 stainless steel.
Machinability
AISI 304 has good machinability, however, its low thermal conductivity means coolants and lubricants should be used liberally, especially on the cutting edges.
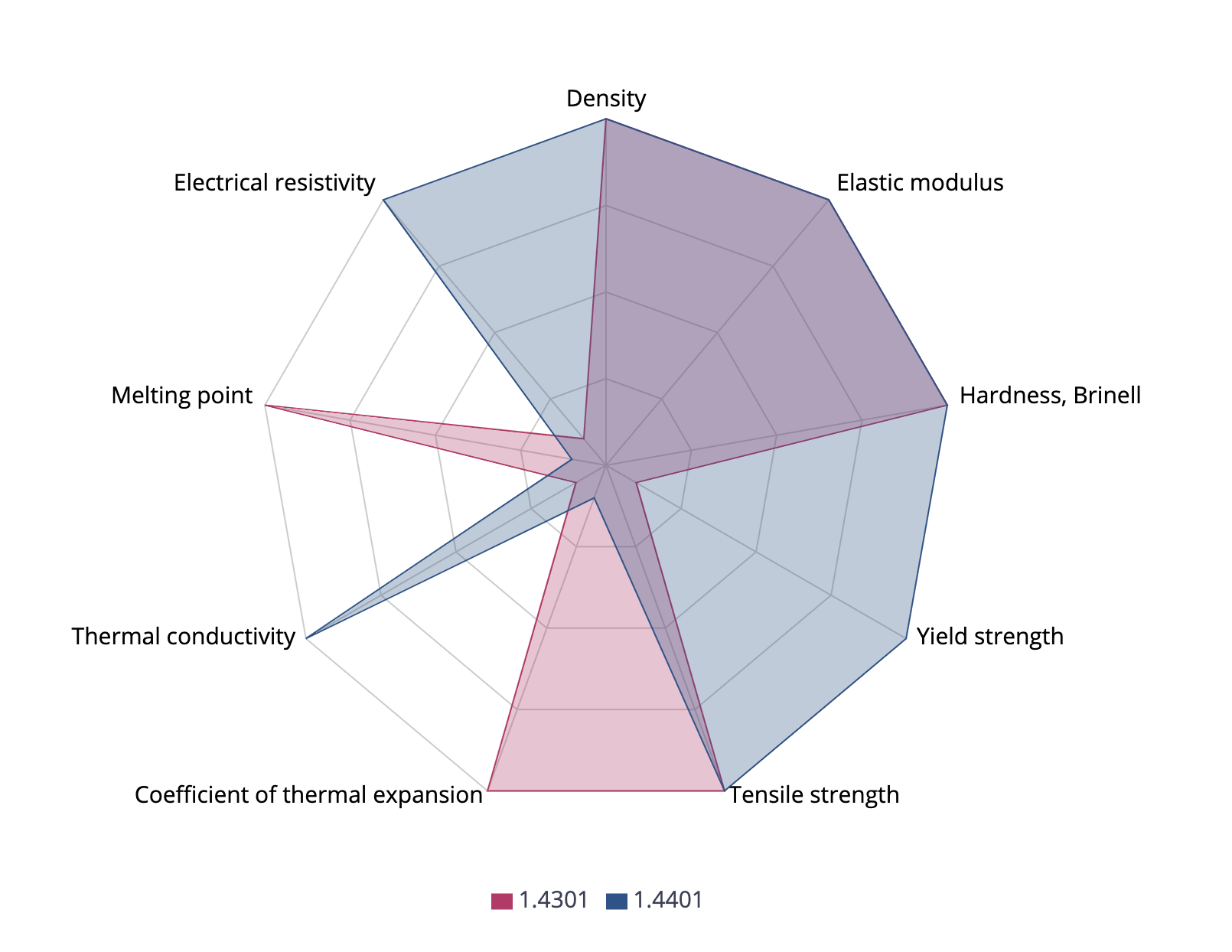
AISI 304 (1.4301) vs AISI 316 (1.4401)
AISI 304 and 316 have similar values for hardness (Brinell), elastic modulus and tensile strength. However, AISI 316 has a slightly higher yield strength at 200 MPa (vs. 190 MPa for 304), while AISI 304 has a slightly higher melting point (1450°C vs. 1400°C for 316). Generally, AISI 316 has better corrosion resistance than AISI 304.
Suppliers of AISI 304 stainless steel
Matmatch works with stainless steel suppliers around the world. You can find a selection of suppliers below and contact them from their profile page:
Company |
About the supplier |
|
Deutsche Edelstahlwerke is a leading producer of special steel long products. Acidur 4301 is their version of standard 304 stainless steel. |
|
|
Based in Groningen in the Netherlands, Salomon's distributes a wide range of metals with a focus on Europe. |
|
|
Sverdrup is a global supplier of high-performance materials, including AISI 304. Their headquarters are in Stavanger, Norway. |
|
|
Ambica Steels is headquartered in India but has sales offices around the world, including in Italy, Germany, Turkey, Australia, and Peru. |
FAQs about AISI 304 Stainless Steel
Here are some of the frequently asked questions about AISI 304.
What type of stainless steel is AISI 304?
AISI 304 is an austenitic stainless steel grade that belongs to the 300 series.
What does AISI stand for in stainless steel?
AISI stands for American Iron and Steel Institute, which developed a standardised numbering system for stainless steel together with SAE International (a standards organisation).
Is AISI 304 the same as SS 304?
AISI 304, SS 304, SAE 304, and SUS 304 are all different representations of the same material, depending on where it is referenced. SS stands for "stainless steel", SUS stands for "steel use stainless" (Japanese standard), and AISI/SAE refer to the standard organisations that developed the numbering system.
Is AISI 304 magnetic?
Being an austenitic stainless steel, AISI 304 is theoretically non-magnetic. In reality, it is only slightly magnetic. Its nickel content is what helps lower its responsiveness to external magnetic fields.
If you've enjoyed reading this article, you can also read more related content here: